Exploring the Leading Open-Source LLMs of 2024: Innovations and Applications

Background
The transformative wave of generative AI is powered by a core technology known as Large Language Models (LLMs). Built on the transformer architecture, LLMs are adept at understanding and generating human language. Their “large” designation comes from the vast number of parameters, stretching into billions, that these models leverage, trained on extensive text datasets.
Among the key players in the chatbot arena are ChatGPT, utilizing OpenAI’s GPT-4, and Google Bard, based on Google’s PaLM 2 model. These proprietary models have set benchmarks in the industry. However, they come with their share of limitations, including accessibility, transparency, and the potential for innovation constraints, given their proprietary nature.
This backdrop has given rise to an increasing interest in open-source LLMs. These models aim to democratize access to generative AI technology, offering an open, transparent, and collaborative approach to development. This article delves into the top open-source LLMs of 2024, including an exciting new entrant, Chat-completion by novita.ai, marking significant strides in the field.
Advantages of Using Open-Source LLMs
The adoption of open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) is not just a trend but a significant shift towards more ethical, accessible, and sustainable AI development practices. Each aspect of open-source advantages merits a deeper exploration to understand its impact on the AI landscape.
Enhanced Data Privacy and Security
The pivot towards open-source LLMs places data privacy and security in the hands of the organizations using them. Unlike proprietary models, where data might be processed and stored on external servers, open-source models can be run on private infrastructure. This control reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, as companies can implement their security protocols, comply with data protection regulations more easily, and assure their clients of data integrity. Moreover, the open-source community actively scrutinizes code, making it possible to identify and rectify vulnerabilities swiftly, further bolstering security.
Cost Efficiency
While the initial allure of open-source LLMs might be the absence of licensing fees, the narrative around cost efficiency is nuanced. Open-source models provide a foundation upon which businesses, especially startups and small to medium enterprises (SMEs), can build custom solutions without the burden of high upfront costs. However, the operational costs, including computational resources for training and inference and potential cloud storage fees, must be carefully considered. Despite these costs, the open-source model still stands out for its potential for significant savings over time, offering a scalable solution that can grow with a company’s needs without the constraints of licensing limitations.
Customization and Transparency
Open-source LLMs offer an unparalleled level of customization and transparency. Access to the model’s source code and architecture not only enables businesses to tailor the LLM to their specific needs but also allows for a deeper understanding of how the model makes decisions. This transparency is crucial for trust in AI systems, especially in sensitive applications such as healthcare, finance, and legal services. Customization can range from adjusting the model for different languages or dialects to fine-tuning it for specialized tasks, providing a versatility that proprietary models cannot match.
Community-Driven Innovation
The open-source model thrives on collaboration and shared knowledge. It harnesses the collective expertise of developers, researchers, and users worldwide to drive innovation at an unprecedented pace. This communal approach accelerates the evolution of LLMs, as contributions range from bug fixes and feature enhancements to comprehensive improvements in model architecture. Such collaboration not only speeds up technological advancement but also democratizes AI development, making cutting-edge technology accessible to a broader audience.
Sustainable AI Development
Sustainability in AI development is a growing concern, with the environmental impact of training large-scale models under scrutiny. Open-source LLMs contribute to a more sustainable approach in several ways. Firstly, the shared development model encourages the efficient use of resources, as improvements in code and architecture can lead to reduced computational requirements. Secondly, transparency in open-source projects means that the environmental costs of training and running these models are more openly discussed, fostering a community ethos of resource-conscious development. Lastly, the open-source community is well-positioned to innovate in the area of green computing, seeking ways to minimize the carbon footprint of AI technologies.
6 Top Open-Source Large Language Models For 2024
- LLaMA 2 by Meta

Launched for both research and commercial applications in July 2023, LLaMA 2 is an advanced pre-trained generative text model that ranges from 7 to 70 billion parameters. It has been enhanced through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), making it versatile enough for a wide array of natural language generation tasks. This includes everything from chatbot functionalities to complex programming assignments. Meta has expanded the utility of LLaMA 2 by introducing specialized versions such as Llama Chat and Code Llama, tailored for specific applications.
- Bloom

Debuted in 2022 after a collaborative effort that spanned a year and engaged volunteers from over 70 countries, alongside researchers from Hugging Face, BLOOM represents an autoregressive LLM designed to extend text based on a given prompt, utilizing massive datasets and industrial-level computing power.
Its introduction was a significant step towards making generative AI more accessible to all. Boasting 176 billion parameters, BLOOM stands as one of the most formidable open-source LLMs available, capable of generating cohesive and precise text across 46 languages and 13 programming languages.
At the core of BLOOM lies a commitment to openness, with the project’s source code and training data made available to the public. This transparency ensures that anyone can use, examine, and enhance the model.
- BERT by Google

Google unveiled BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) as an open-source LLM in 2018. It quickly set new standards for a range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks with its cutting-edge capabilities.
BERT’s innovative approach in the initial stages of LLM development, coupled with its availability as an open-source tool, propelled it to widespread popularity and adoption. By 2020, Google had integrated BERT into Google Search across more than 70 languages, highlighting its effectiveness.
Today, the community benefits from a multitude of open-source, readily available BERT models tailored for specific applications, including sentiment analysis, medical record interpretation, and identifying harmful content.
- Falcon 180B

Launched in September 2023 by the Technology Innovation Institute of the United Arab Emirates, Falcon 180B operates with 180 billion parameters and processes 3.5 trillion tokens. This remarkable level of computational capability has enabled Falcon 180B to surpass the performance of LLaMA 2 and GPT-3.5 across a variety of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Moreover, Hugging Face has indicated that Falcon 180B is poised to compete with Google’s PaLM 2, the engine behind Google Bard.
While Falcon 180B is accessible at no cost for both commercial and research purposes, it’s crucial to acknowledge that significant computing resources are necessary for its operation.
- GPT-NeoX and GPT-J

Crafted by the team at EleutherAI, a non-profit dedicated to AI research, GPT-NeoX and GPT-J emerge as noteworthy open-source alternatives to the well-known GPT series.
GPT-NeoX boasts a substantial 20 billion parameters, and GPT-J follows with a solid 6 billion parameters. Despite the fact that the most sophisticated LLMs today are equipped with upwards of 100 billion parameters, both GPT-NeoX and GPT-J manage to achieve high levels of accuracy.
These models benefit from training on 22 distinct, high-quality datasets sourced from a variety of fields, enabling their application across numerous domains and a wide array of tasks. Unlike GPT-3, neither GPT-NeoX nor GPT-J has undergone training with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), distinguishing their development approach.
- Vicuna 13-B

Vicuna-13B is an open-source dialogue model, enhanced by refining the LLaMa 13B framework with real conversational data shared by users through ShareGPT.
Functioning as a sophisticated chatbot, Vicuna-13B’s utility spans numerous sectors, offering significant benefits in customer service, healthcare, education, finance, and the travel and hospitality industry, among others.
Initial assessments, with GPT-4 serving as the benchmark, reveal that Vicuna-13B mirrors over 90% of the effectiveness found in leading models such as ChatGPT and Google Bard, and it surpasses other models, including LLaMa and Alpaca, in the majority of comparisons.
Choosing the Suitable Open-Source LLM
The expanding universe of open-source LLMs presents a plethora of options. Selecting the right model depends on your objectives, such as the specific tasks at hand, desired accuracy, budget constraints, and whether a pre-trained model can meet your needs. Innovations like Chat-completion by novita.ai highlight the sector’s dynamic nature, offering tailored solutions that drive forward the possibilities of conversational AI.
Disadvantages of Open-Source LLM
- Quality Control: Open-source LLMs might lack stringent quality control mechanisms compared to proprietary models. This could result in inconsistencies or inaccuracies in generated text, as they may not undergo the same level of scrutiny or refinement.
- Security Concerns: Open-source projects are susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Malicious actors could exploit weaknesses in the codebase to introduce malware or compromise user data.
- Lack of Support: Users of open-source LLMs may not have access to dedicated customer support or assistance in troubleshooting issues. This can be a challenge, particularly for non-technical users who may require guidance.
- Limited Resources: Open-source projects often rely on volunteer contributions, which may result in slower development cycles or limited resources for maintenance and updates.
- Intellectual Property Risks: Contributors to open-source projects may inadvertently introduce copyrighted or proprietary code, leading to legal issues or conflicts over intellectual property rights.
- Fragmentation: With multiple open-source LLM projects available, users may face fragmentation in terms of features, compatibility, and community support. This can lead to confusion and difficulties in selecting the most suitable option.
- Dependency Management: Open-source LLMs may have dependencies on other libraries or frameworks, which can introduce complexity and compatibility issues, especially when integrating with existing software systems.
- Documentation and Training: Open-source projects may lack comprehensive documentation or formal training resources, making it challenging for users to fully understand and leverage the capabilities of the LLM.
- Sustainability: Without a clear funding model or sustainable revenue stream, open-source LLM projects may struggle to maintain long-term viability, potentially leading to abandonment or discontinuation of support.
- Ethical Considerations: While open-source LLMs promote transparency and collaboration, they also raise ethical concerns regarding data privacy, bias, and the responsible use of AI technologies. Community governance mechanisms may be insufficient to address these complex issues comprehensively.
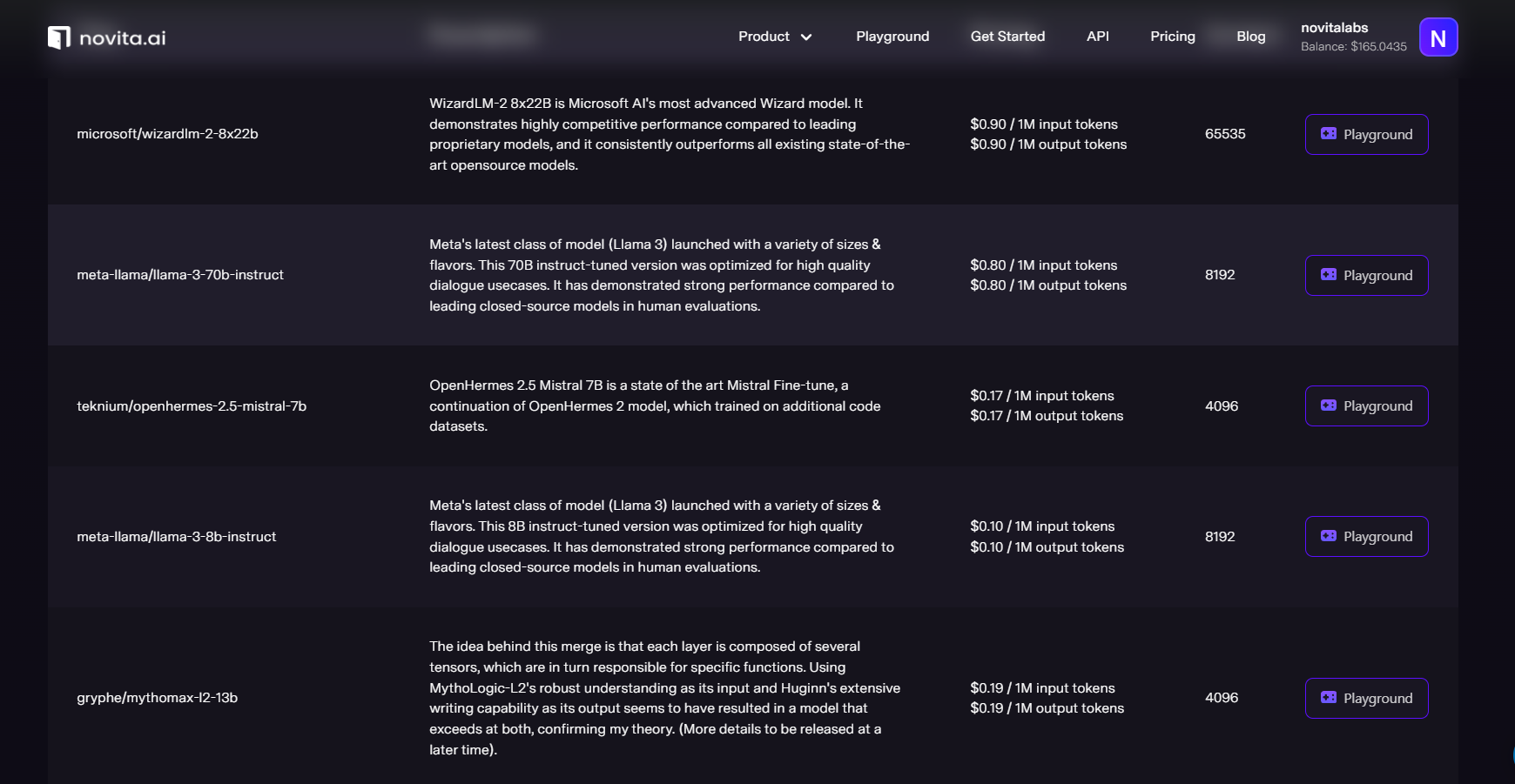
Due to open-source LLMs have such disadvantages, users and developers would choose paid LLM APIs to avoid them. For example, Novita AI LLM offers uncensored, unrestricted conversations through powerful Inference APIs. With cost-efficient Pricing and scalable models, Novita AI LLM Inference API empowers LLM high stability and rather low latency in less than 2 seconds.
Conclusion
The landscape of open-source LLMs in 2024 is vibrant and diverse, offering promising alternatives to proprietary models. With models like Chat-completion by novita.ai entering the fray, the space is set for further innovation, making generative AI technologies more accessible and customizable than ever before. This shift not only fosters a collaborative ecosystem but also paves the way for groundbreaking advancements in AI-driven communication and beyond.
novita.ai, the one-stop platform for limitless creativity that gives you access to 100+ APIs. From image generation and language processing to audio enhancement and video manipulation,cheap pay-as-you-go , it frees you from GPU maintenance hassles while building your own products. Try it for free.
Recommended reading
Novita.ai vs. Together.ai: A Comprehensive Comparison
Unveiling the Power of Large Language Models: A Deep Dive into Today's Leading LLM APIs
The Ethical Frontier: Analysing the Complexities of NSFW AI